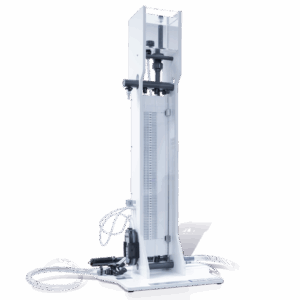
C6-MKII-10 – Fluid Friction Measurements
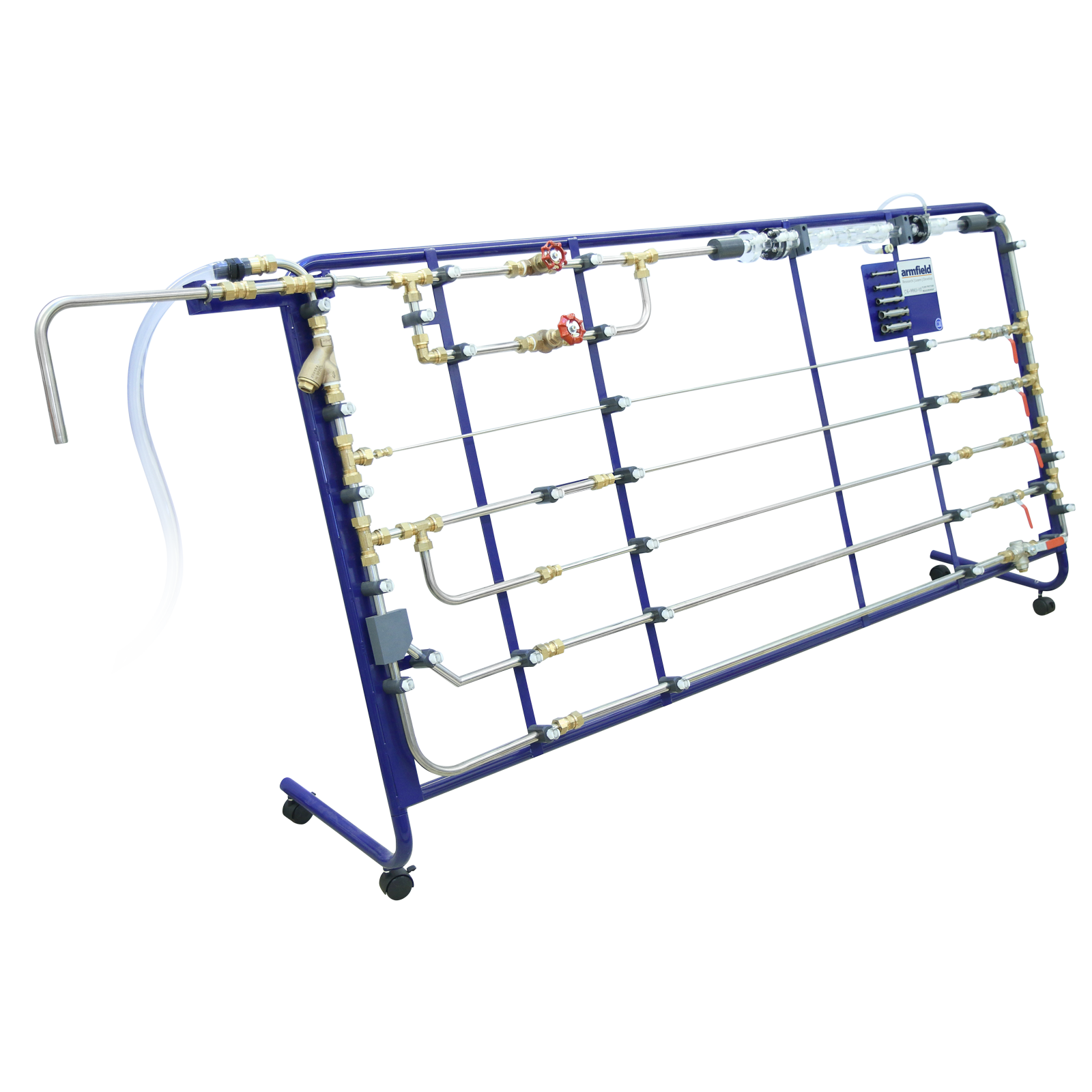
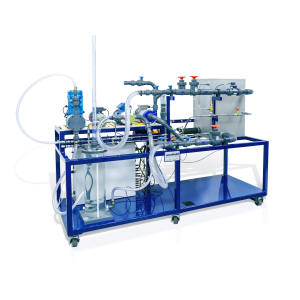
The Armfield C6-MKII-10 Fluid Friction Measurements unit provides facilities for the detailed study of fluid friction head losses, which occur when an incompressible fluid flows through pipes, fittings and flow metering devices.
Pipe friction is one of the classic laboratory experiments and has always found a place in the practical teaching of fluid mechanics.
Description
The Armfield C6-MKII-10 Fluid Friction Measurements unit provides facilities for the detailed study of fluid friction head losses, which occur when an incompressible fluid flows through pipes, fittings and flow metering devices.
Pipe friction is one of the classic laboratory experiments and has always found a place in the practical teaching of fluid mechanics.
With this unit, friction head losses in straight pipes of very different sizes can be investigated over a range of Reynolds’ numbers from10³ to nearly 10⁵. This covers the laminar, transitional and turbulent flow regimes in smooth pipes.
In addition an artificially roughened pipe is supplied, which at the higher Reynolds’ numbers shows a clear departure from the typical smooth bore pipe characteristics.
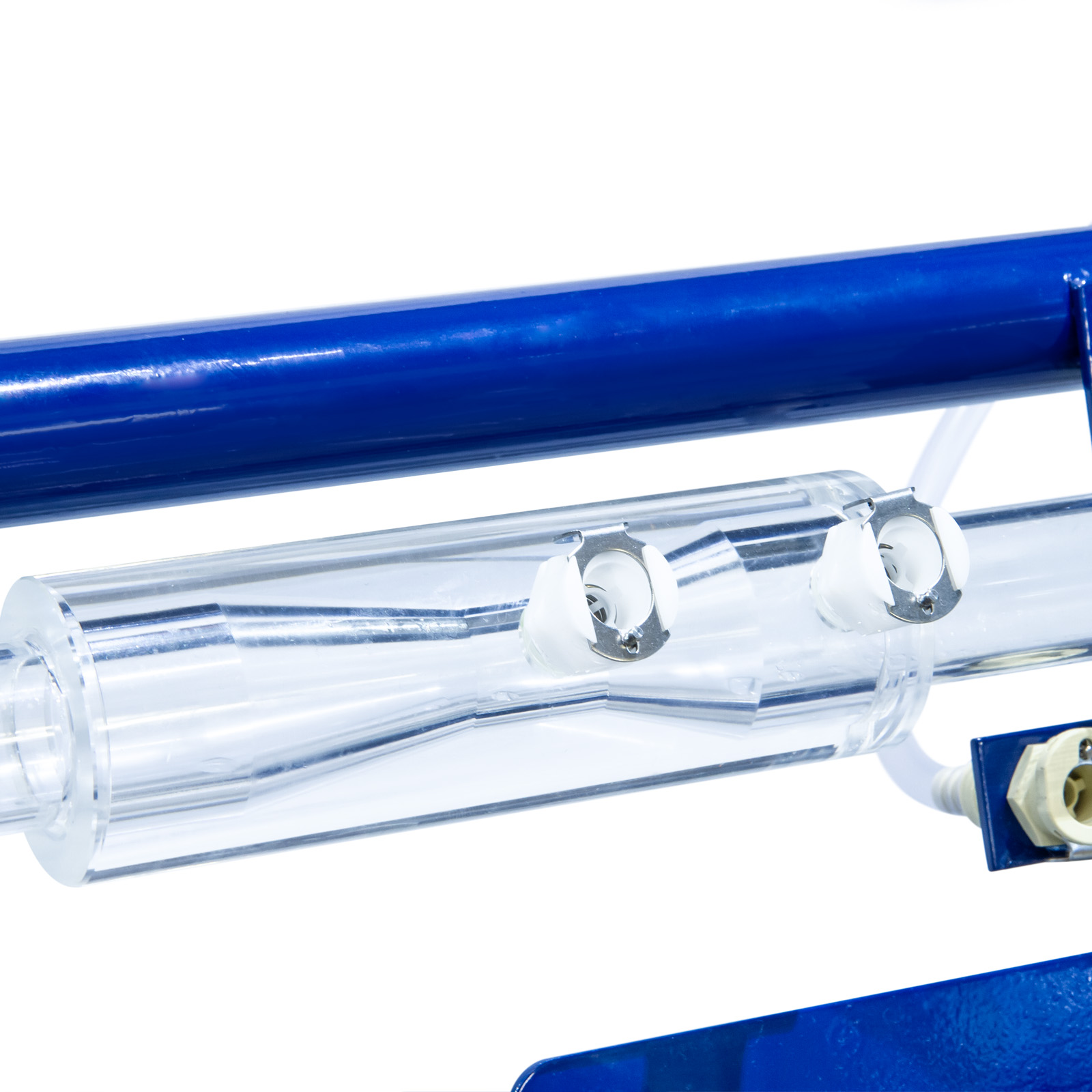
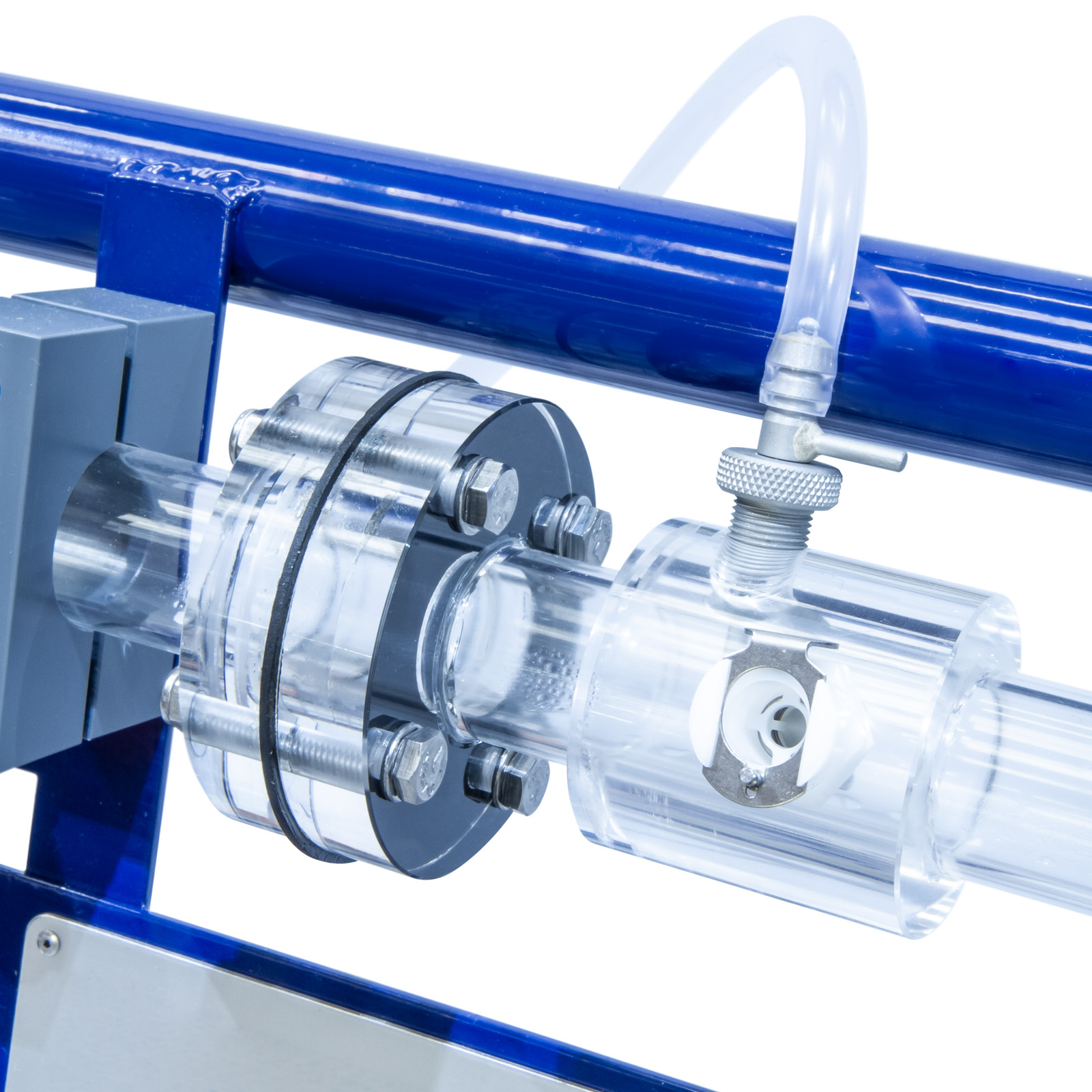
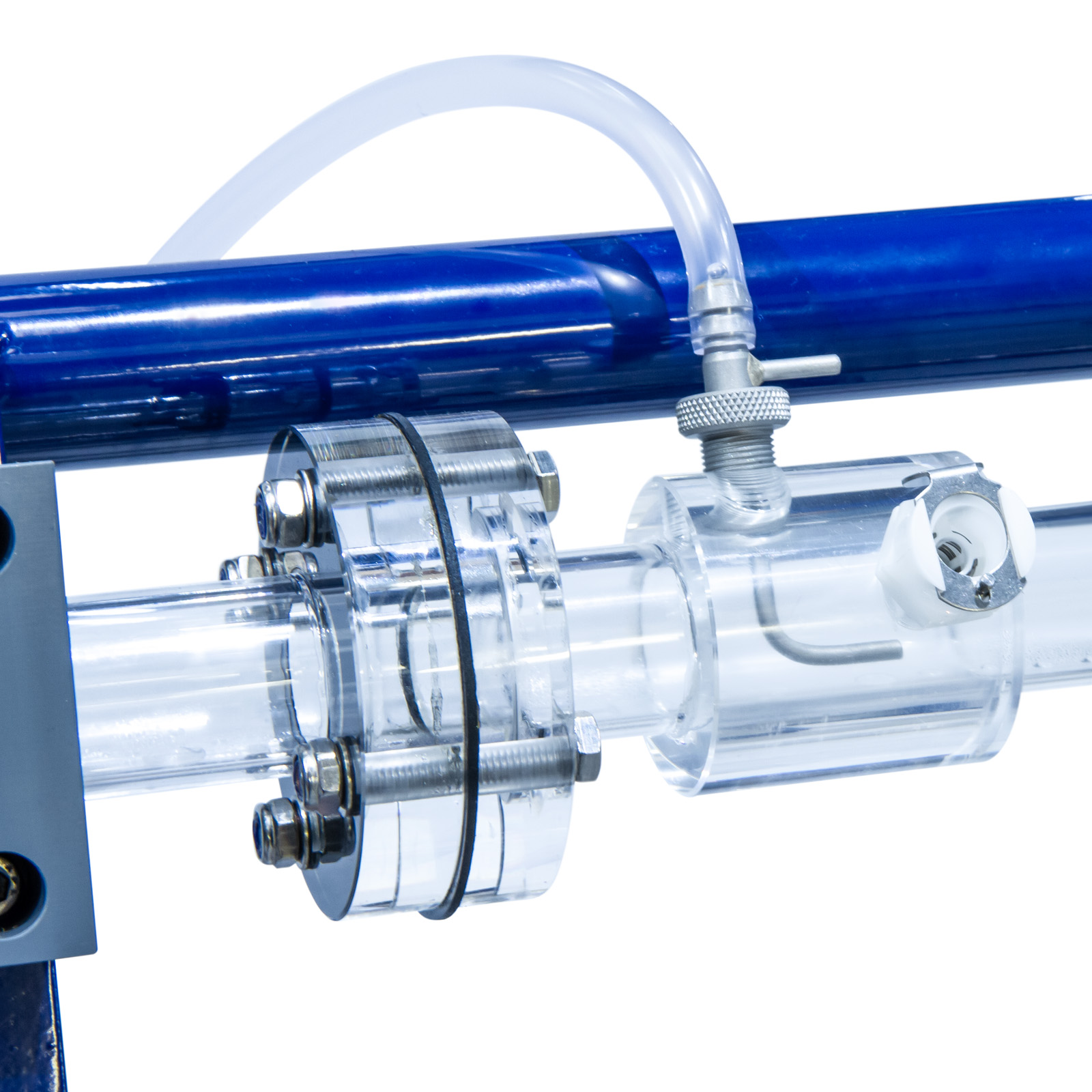
In addition to the equipment for the study of losses in straight pipes, a wide range of accessories are included such as pipe fittings and control valves, a Venturi tube, an orifice plate assembly and a Pitot tube.
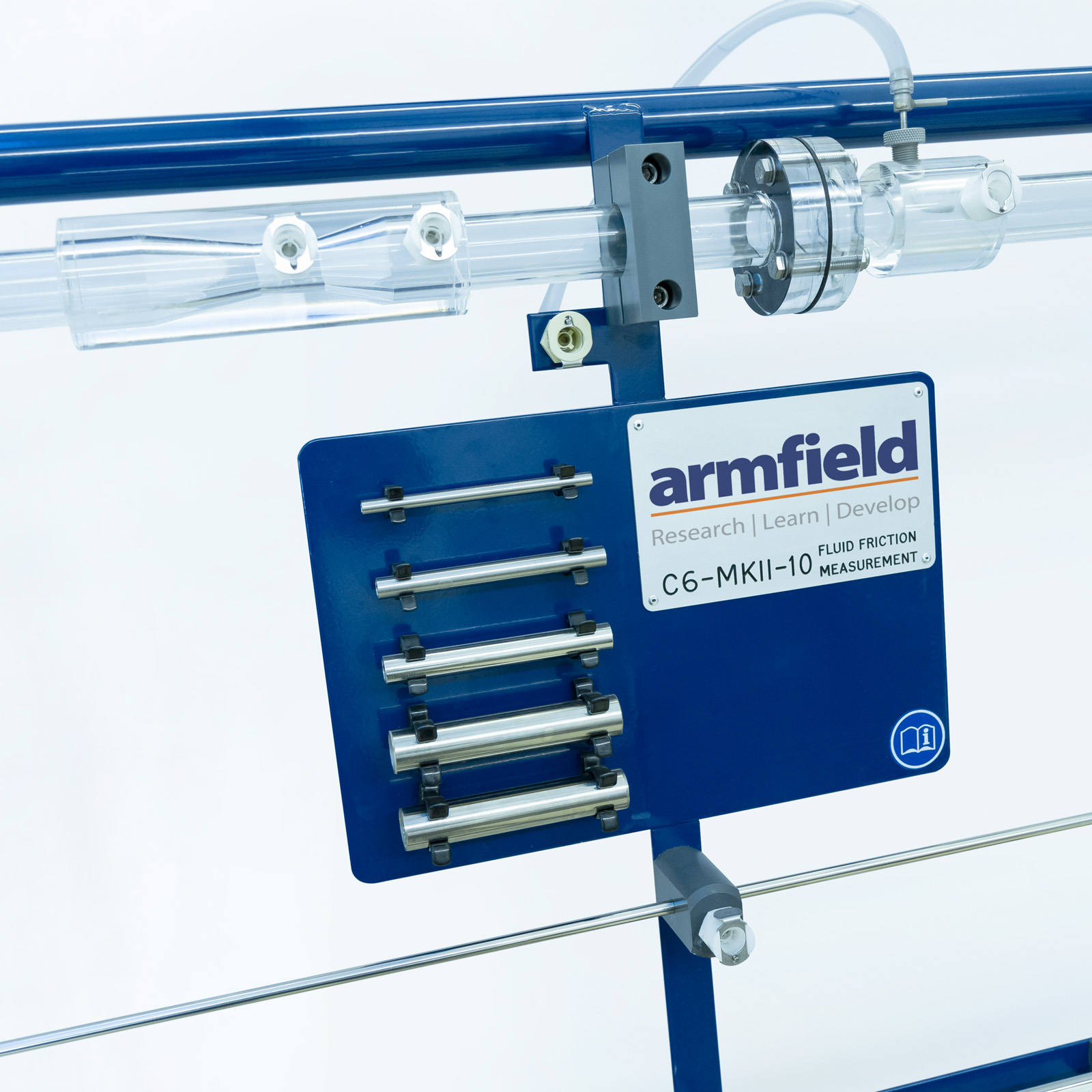
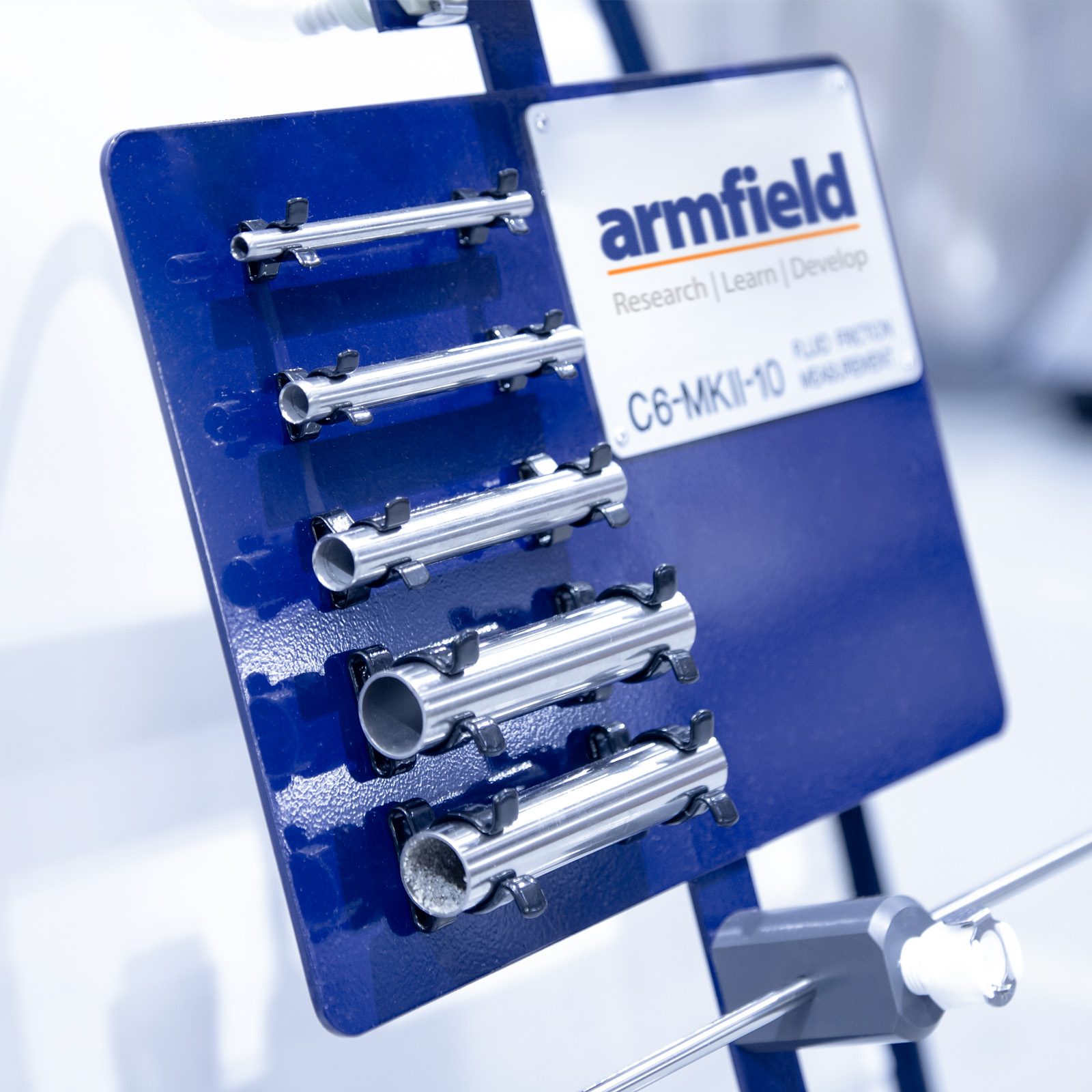
An arrangement of six pipes provides facilities for testing the following:
- Four smooth bore pipes of different diameters
- Artificially roughened pipe
- 90° bends (large & small radii)
- 90° elbow
- 90° mitre
- 45° elbow
- 45°Y
- 90°T
- Sudden enlargement
- Sudden contraction
- Gate valve
- Globe valve
- Ball valve
- Inline strainer
- Perspex venturi
- Perspex orifice meter
- Perspex pipe section with a pitot tube & static tapping
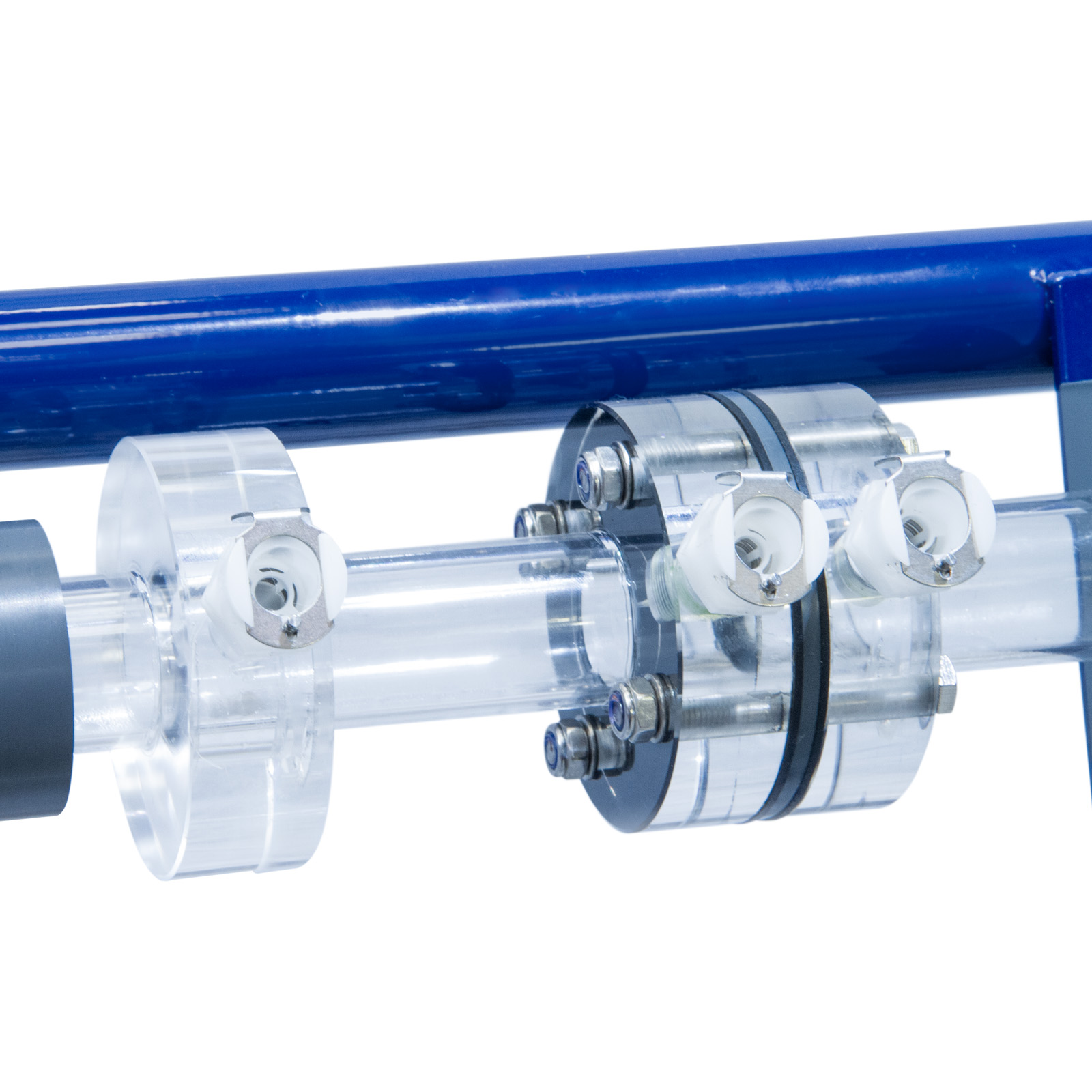
Short samples of each size test pipe are provided loose so that the students can measure the exact diameter and determine the nature of the internal finish.
The ratio of the pipe diameter to the distance of the pressure tappings from the ends of each pipe has been selected to minimise end and entry effects. A system of isolating valves is provided whereby the pipe to be tested can be selected without disconnecting or draining the system. This arrangement enables tests to be conducted on parallel pipe configurations.
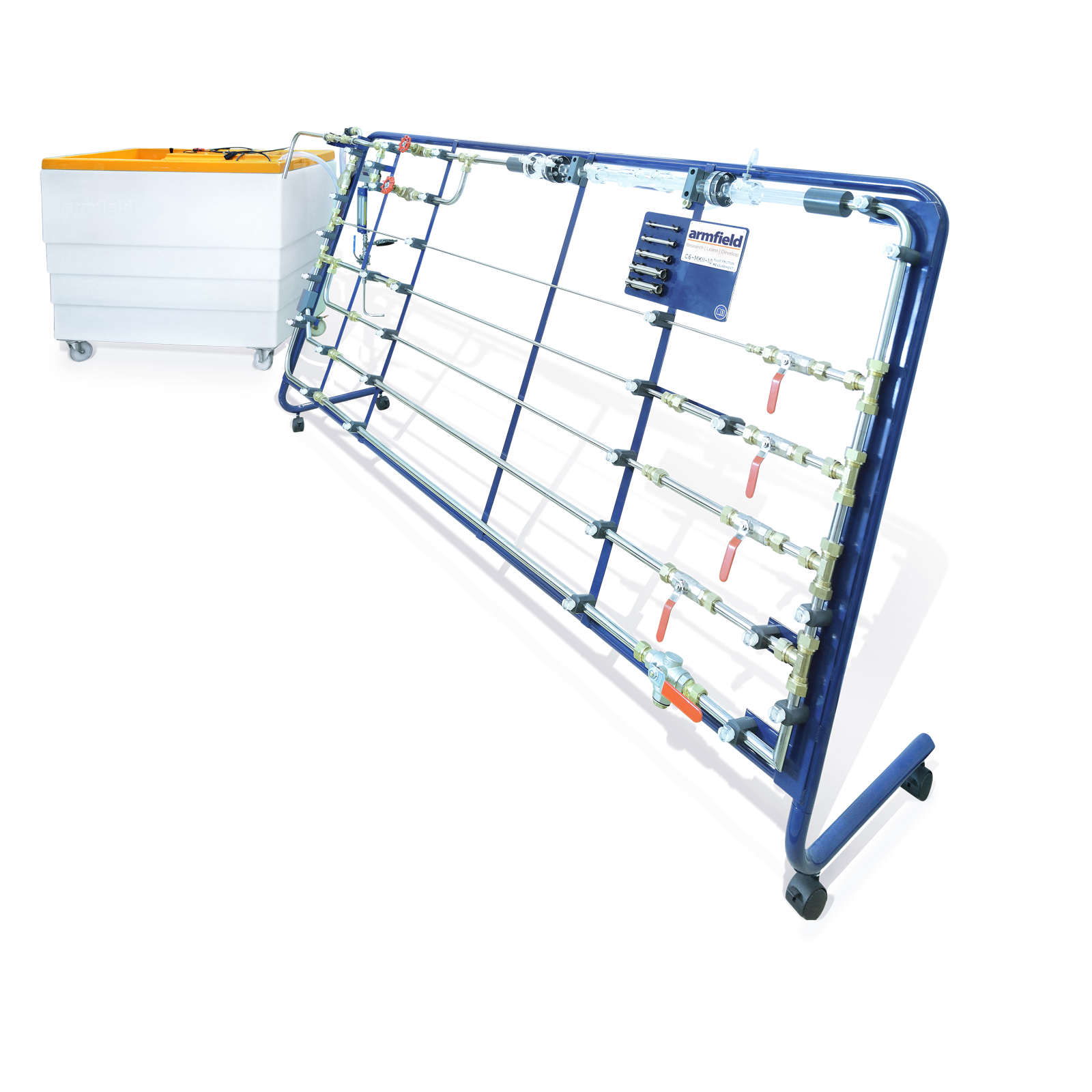
An optional floor-standing Hydraulics Bench incorporates a sump tank and volumetric flow measurement facility. Rapid and accurate flow measurement is possible over the full working range of the apparatus.
The level rise in the measuring tank is determined by an independent sight gauge. A 250ml capacity glass measuring cylinder is supplied for measuring the flow rate under laminar conditions (very low flows).
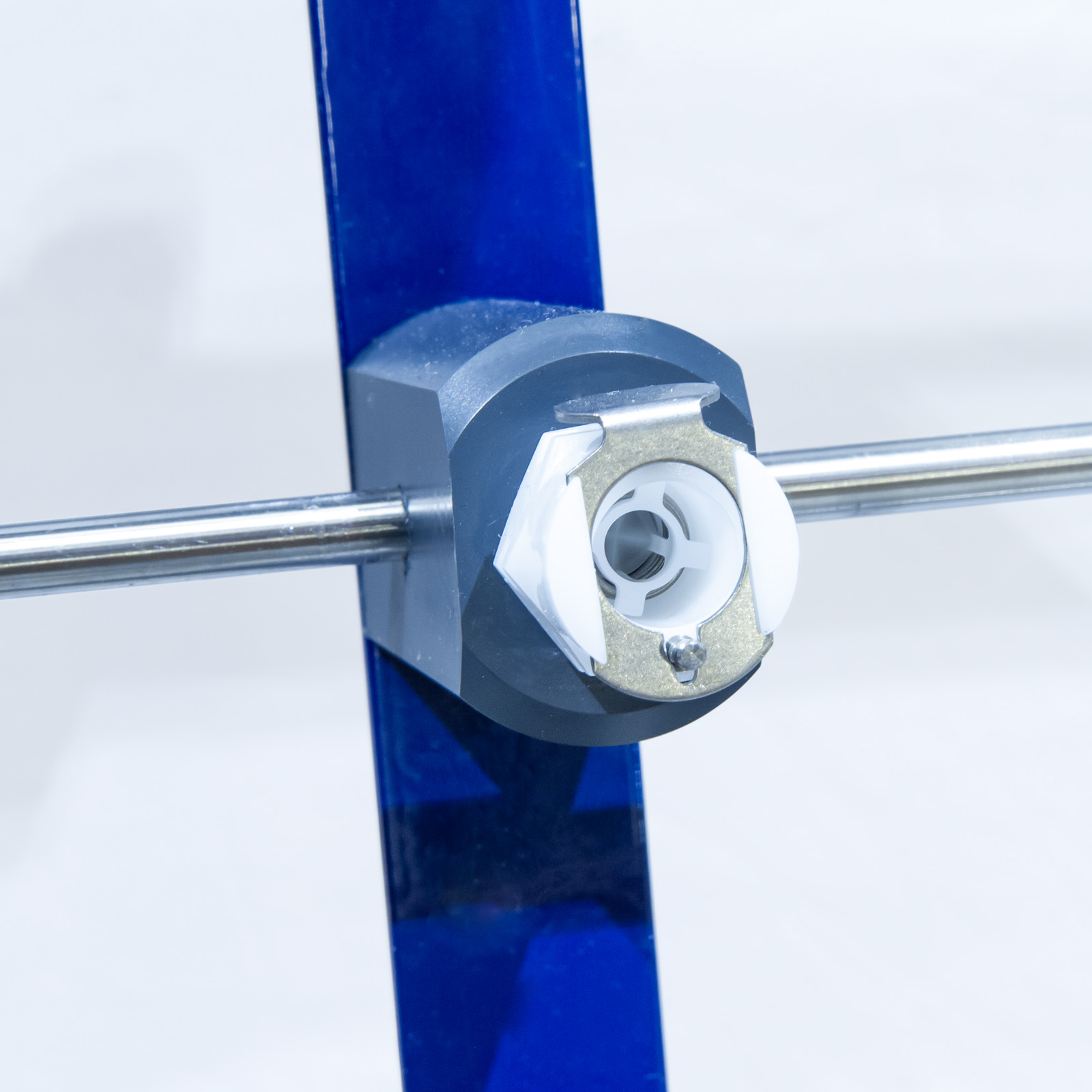
Each pressure tapping is fitted with a quick action self-sealing connection. Probe attachments with an adequate quantity of translucent polythene tubing are provided so that any pair of pressure tappings can be rapidly connected.
All the test pipes and fixed interconnecting pipes are fabricated in stainless steel.
Technical details for test pipes:
Diameter:
Distance between tappings: 1m
Number of tapping points: 38
Technical Specifications
- A unit for the detailed study of fluid friction head losses, which occur when an incompressible fluid flows through pipes, fittings and flow metering devices
- A substantial floor-standing tubular steel frame supports test circuits comprising:
– Four smooth-bore pipes of different diameters ranging from 4.5mm ID to 17.2mm ID
– Artificially roughened pipe
– 90° bends (large & small radii)
– 90° elbow
– 90° mitre
– 45° elbow, 45°Y, 90°T
– Sudden enlargement
– Sudden contraction
– Gate valve
– Globe valve
– Ball valve
– Inline strainer
– Perspex venturi
– Perspex orifice meter
– Perspex pipe section with a pitot tube & static tapping
– 38 tapping points - All fixed pipes fabricated in stainless steel
- Suitable for studying Reynolds’ numbers from 10³ to nearly 10⁵
- A system of isolating valves, quick-release manometer connection valves and self-sealing pressure tappings ensure fast, accurate results
- Data logging accessory available
- Computer aided learning program available
- A user instruction manual provides installation, commissioning and maintenance data, together with student exercises
- The unit is designed for use with a Hydraulics Bench (F1-10)
Features & Benefits
A wide range of measurements, demonstrations and training exercises are possible with the equipment:
- Confirming the relationship between head loss due to fluid friction and velocity for flow of water
- Determining the head loss associated with flow through a variety of standard pipe fittings
- Determining the relationship between pipe friction coefficients and Reynolds’ number for flow through a pipe with roughened bore
- Demonstrating the application of differential head devices in the measurement of flow rate and velocity
- Providing practical training of pressure measurement techniques
- Enhancing understanding of the hydraulic principles involved through the use of complementary computer software
In order to complete the full range of experiments possible with the C6MkII, it is necessary to measure pressures over a greater range than a single instrument can provide.
Armfield recommend the use of a water manometer for the low-pressure measurements and an electronic pressure meter for the high-pressure measurements.
Order Codes:
Also available for use with data acquisition instruments is a software package, which performs all the necessary calculations from readings entered manually.
Order code:
uC6-MkII-ABASIC: Educational software for fluid friction measurements (manual data entry)
uAutomatic Data AcquisitionC6-MkII-DTA-ALITE: Computer Data Capture Unit
The C6-MkII-DTA-ALITE is a small data logging unit, which enables the recording of data to a suitable PC (not supplied).
The unit comprises an interface device with USB port and cable, a turbine-type flow meter complete with associated pipework, and two independent pressure sensors with quick-release fittings.
The 32/64-bit compatible software features real-time data display on a mimic diagram of the apparatus, tabular and graphical display of logged data and calculated parameters, plus full educational help texts detailing operational procedures and practical exercises.
Note: The electrical sensors supplied with the C6MkII have been selected to measure over the full range of the C6 pressures and flow rates. However, in order to obtain accurate results at very low flows or differential pressures, it may be necessary to use a volumetric flow measurement method and/or a pressurised water manometer.
- F1-10: Hydraulics Bench
- H12-8-1: Digital Pressure Meter
- H12-2: Liquid Manometer
- C6-MkII-A-BASIC: Education software for manual data entry
- C6-MkII-DTA-ALITE: Data logging accessory with software for C6-MkII
Complementary products
- C1-MkII: Compressible Flow Bench
- C2: Subsonic Wind Tunnel
- C3-MkII: Multi-pump Test Rig
- C4-MkII: Multi-purpose Flume
- C7-MkII: Pipe Surge and Water Hammer
- C9: Flow Meter Demonstration Unit
- C10: Laminar Flow Table
- C11-MkII: Flow in Pipe Networks
- F1-18: Energy Losses in Pipes
- F1-21: Flow Meter Demonstration
- F1-22: Energy Losses in Bends
- A unit for the detailed study of fluid friction head losses, which occur when an incompressible fluid flows through pipes, fittings and flow metering devices
- A substantial floor-standing tubular steel frame supports test circuits comprising:
– Four smooth-bore pipes of different diameters ranging from 4.5mm ID to 17.2mm ID
– Artificially roughened pipe
– 90° bends (large & small radii)
– 90° elbow
– 90° mitre
– 45° elbow, 45°Y, 90°T
– Sudden enlargement
– Sudden contraction
– Gate valve
– Globe valve
– Ball valve
– Inline strainer
– Perspex venturi
– Perspex orifice meter
– Perspex pipe section with a pitot tube & static tapping
– 38 tapping points
- All fixed pipes fabricated in stainless steel
- Suitable for studying Reynolds’ numbers from 10³ to nearly 10⁵
- A system of isolating valves, quick-release manometer connection valves and self-sealing pressure tappings ensure fast, accurate results
- Data logging accessory available
- Computer aided learning program available
- A user instruction manual provides installation, commissioning and maintenance data, together with student exercises
- The unit is designed for use with a Hydraulics Bench (F1-10)
F1-10 Hydraulics Bench
Electrical supply: The F1-10 requires an electrical supply, please refer to the F1 data sheet for details.
F1-10-A: 220-240V / 1ph / 50Hz / 10A
F1-10-B: 110-120V / 1ph / 60Hz / 10A
F1-10-G: 220V / 1ph / 60Hz / 10A
F1-10-2-A: 220-240V / 1ph / 50Hz / 10A
F1-10-2-B: 110-120V / 1ph / 60Hz / 10A
F1-10-2-G: 220V / 1ph / 60Hz / 10A
Recommened instruments
- Stop watch
- Vernier calliper
Minimum computer requirements
The C6-MkII-ABASIC and the C6-MkII-DTA-ALITE require a PC, running Windows 7 or above and a spare USB port (not supplied by Armfield).

PACKED AND CRATED SHIPPING SPECIFICATIONS
Volume: 1.4m³
Gross Weight: 165Kg
Length: 2.250m
Width: 0.470m
Height: 1.190m
C6-MkII-10: Basic Fluid Friction Measurements
This comprises the framework containing the pipes and fittings. It requires an Armfield F1-10 Hydraulics Bench plus an instrumentation system (see below).