Pitot Tubes and Their Role in Aviation

What Are Pitot Tubes?
Pitot tubes are ingenious devices used to measure fluid flow velocity, particularly in aviation, automotive industries, and meteorological applications. Invented by the French engineer Henri Pitot in the early 18th century, these tubes have become an indispensable tool for calculating airspeed, fluid flow rate, and even dynamic pressure. Their role in flight safety and efficiency cannot be understated, making them a cornerstone of modern aerodynamics.
A Brief History of Pitot Tubes
Henri Pitot’s original invention was designed to measure the velocity of water in rivers. Over time, this simple yet effective design evolved into more sophisticated versions, such as pitot-static tubes, which are now integral to aircraft instrumentation. These advancements have enabled accurate airspeed measurements, contributing to the safety and performance of countless vehicles and systems.
Types of Tubes
There are several types of tubes, each suited to specific applications:
- Traditional Tubes: These measure the stagnation pressure of a fluid and are often paired with a static port to calculate flow velocity.
- Pitot-Static Tubes: These combine both pitot and static pressure measurements, offering greater accuracy in calculating airspeed and other parameters.
- Multi-Port Tubes: These advanced versions are used for more complex measurements, such as determining fluid flow in varying conditions.
Armfield provides a range of H30 pitot tubes to meet diverse requirements, ensuring precision and reliability across all applications.
How A Pitot Tube Works
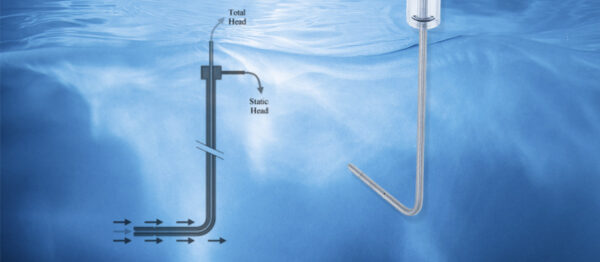
The tubes operate based on Bernoulli’s equation, which relates the pressure of a fluid to its velocity. The device captures both the total pressure (stagnation pressure) and the static pressure. The difference between these pressures, known as dynamic pressure, is used to calculate the flow velocity. For aviation, pitot-static systems play a crucial role in measuring airspeed, which is displayed as indicated airspeed on an aircraft’s instrumentation panel.
See: F1-33 Demonstrator

Applications of the Tubes
Pitot tubes are incredibly versatile, finding use in:
- Aviation: Measuring airspeed and other flight parameters.
- Automotive Testing: Determining airflow in wind tunnels.
- Weather Instruments: Measuring wind speed and direction.
- HVAC Systems: Monitoring airflow in ducts and vents.
Armfield tubes are expertly designed to study these diverse fields.
Maintaining and Calibrating Pitot Tubes
Regular maintenance and calibration of pitot tubes are essential for reliable performance. Here are some tips:
- Prevent Blockages: Ensure the pitot tube’s openings are free of debris and contaminants.
- Calibrate Regularly: Calibrate the manometer connected to the tubes.
- Inspect for Damage: Check for signs of wear, especially in high-velocity applications.
Armfield offers comprehensive calibration and maintenance services, providing peace of mind to our customers.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite their robust design, pitot tubes can encounter problems, such as:
- Icing: In cold conditions, ice can block the openings, leading to inaccurate readings.
- Pressure Loss: Damage or wear can result in incorrect pressure measurements.
- Misalignment: Improper installation can affect performance.
Our team at Armfield provides expert support and guidance to address these issues, ensuring optimal performance of your pitot systems.
Pitot FAQs
1. Who was Henri Pitot, and what was his contribution?
Henri Pitot was a French engineer who invented these tubes to measure fluid velocity in rivers. His work laid the foundation for modern fluid dynamics.
2. How do pitot tubes measure flow velocity?
The tubes measure flow velocity by capturing total and static pressures. The difference between these pressures, known as dynamic pressure, is used to calculate velocity using Bernoulli’s equation.
3. What is the difference between pitot-static tubes and traditional pitots?
Traditional tubes measure only stagnation pressure, while pitot-static tubes combine this with static pressure measurements, offering greater accuracy in calculating airspeed and other parameters.
4. What are the common applications?
These tubes are used in aviation, automotive testing, meteorology, and HVAC systems to measure airspeed, fluid flow velocity, and dynamic pressure.
The Armfield Advantage
At Armfield, we pride ourselves on providing high-quality solutions for all types of tubes. Our products are designed with precision, reliability, and performance in mind, catering to a wide range of industries. From standard tubes to advanced multi-port designs, we have the expertise and innovation to meet your study needs.
Contact Us Today
Ready to enhance your operations with reliable pitot solutions? Contact Armfield today to learn more about our products and services.
You may also like:
- Exploring Cantilever Span Bridges and How They work
- Fans and Compressors: Designed For Engineering Education
- Log a Fault or Functionality Query with Your Armfield Hardware Product
- The Science of Carbonation and Armfield’s FT102X

Armfield can trace its history back over 130 years, throughout which, the Company’s policy of quality, innovation and service has helped it to maintain a strong market position and develop a reputation for industry leadership in the field of Engineering teaching.
Education Division
Operating since 1963, the Armfield Education Division designs and manufactures equipment for engineering education and research.
Industrial Division
The Armfield Industrial Division designs and manufactures research & development systems, primarily for the food, beverage, dairy, edible oil and pharmaceutical industries.




































One thought on “Pitot Tubes and Their Role in Aviation”
Comments are closed.